What is Dip Moulding
You are here: Dip Moulding /What is Dip Moulding
Dip Moulding
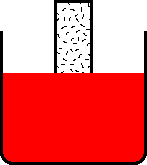
Dip molding is a plastic manufacturing process where a heated metal mandrel(mold) is immersed in a tank of molten polymer resin such as plastisol. The plastic is coated/formed around the mold. The hotter the mold and the longer the dip, the thicker the coating. The mold is then extracted from the bath and goes through a curing or cooling process. The part is stripped from the mold after is cured or solidified. Even parts on complicated molds can be stripped relatively easily because the material is quite elastic. The part may need to be dipped more than once to achieve the desired thickness.
Examples of dip molded products are :
Insulation Shrouds
Bellows
Connector Covers
Coupler Covers
Battery Caps
handlebar grips
Protection Caps
Plastisol is the most common dip molding material. It is a mixture of suspended plastic particles (usually PVC) dispersed in a plasticizer. As a liquid, it can be stored at room temperature for years. Once heated, the two components fuse into a vinyl, never to liquify again. Plastisol can be formulated to produce vinyls with almost any durometer, clarity, color, and a variety of chemical and electrical properties.
Other common candidates for dip molding are latex, neoprene, urethane, epoxy, etc. Recently, polyurethane and Silicone are often used to replace latex to avoid allergy related issues.
To control the thickness and the quality of the finish, the following parameters need to be carefully managed in the dip molding process: Temperature of the mold , Temperature of the resin , Speed of dip-in , Bath time and Withdraw speed.